AI system targets tree pollen behind allergies
Imagine trying to tell identical twins apart just by looking at their fingerprints. That's how challenging...

Not in the mood: Mercury messes with songbirds' mating game
Before they can fight to survive, some endangered songbirds are losing their groove and being robbed...
Saving the kākāpō from 'crusty bum': Study identifies bacterial culprits
Relief may be in sight for kākāpō affected by an extremely painful disease, thanks to a...
Long-term field experiment shows combined approach can maximize benefits of grassland restoration
Results from a long-term field experiment shed new light on how grasslands can be restored for...
Invasive rats and rainforest mammals are sharing gut microbes as urban areas grow
As urban development continues to creep further into Earth's oldest and most diverse rainforests, a Swansea...
Act now or wait centuries: Marine restoration success hinges on immediate intervention
Marine habitats are facing unprecedented threats, with 66% of coastal areas already altered and degraded. Bottom-contact...
Rhythmically trained sea lion Ronan returns for an encore—and performs as well as humans
Animal research on biomusicality, which looks at whether different species are capable of behaving in ways...
Satellite data and DNA reveal 50-year decline in Greek mountain tea diversity
Increased vegetation growth in European mountains, driven by climate and land-use changes, reduces the genetic diversity...
Sea otters benefit from prey boom triggered by loss of ochre sea stars
New research led by Monterey Bay Aquarium reveals a surprising ripple effect in coastal ecosystems: the...

Palatable versus poisonous: Scientists reveal how bats learn to identify which prey is safe to eat
Scientists at the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (STRI) found that the fringe-lipped bat, known to eavesdrop...
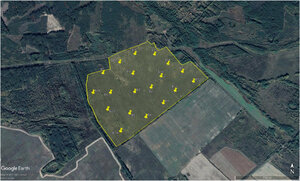
Bringing farms back to Chernobyl-affected lands: New protocol offers hope
Thousands of hectares of Chernobyl-affected farmland, long deemed too dangerous for cultivation in northern Ukraine can...
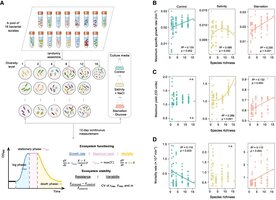
Microbial research suggests that biodiversity does not always increase ecosystem stability
Although many conservationists believe biodiversity is intrinsically valuable, the protection of biodiversity has also been argued...

Popularly eaten fish among key seabed engineers, research shows
Many of the fish we eat play a key role in maintaining the seabed—and therefore our...

Less intensive management works best for agricultural soil, study finds
The less intensively you manage the soil, the better the soil can function; for example, not...

Global map of fishmeal and fish oil factories exposes industry's footprint
Around the world, millions of tons of small fish are processed into fishmeal and fish oil...

Social 'hippie' spiders don't believe in labels
New research led by the University of Portsmouth has revealed that African social spiders—dubbed "hippie spiders"...

Many paths to an angry bird: Female cavity-nesting birds show higher aggression when defending limited nesting sites
"Get off my lawn!" Funny as a meme but maybe scary in real life, this short...

Up to 42% of insect behavioral experiments not reproducible across laboratories
If an experiment is repeated under similar conditions, the results should be the same. In reality,...
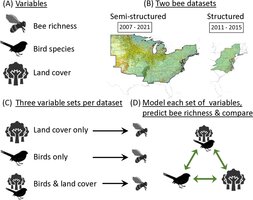
The birds and the bees: Including bird data improves estimates of wild bee species
A study published in the journal PLOS One reveals that combining bird observation data with land...

Animal energy usage made visible through video
Energy scarcity is a central driver of animal behavior and evolution. The amazing diversity of life...

Some male mice fiercely guard females within their territories, while others seek out quick flings
In a comprehensive study conducted at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Biology, researchers tracked 244...

Empathic comforting varies more within bonobo and chimpanzee species than between them
Psychologists from Durham University, UK, have observed the behavior of 90 sanctuary-living apes to establish whether...

Some shark bites may be 'survival instinct' rather than planned attacks, contrary to media portrayal
Sharks are often perceived as the ultimate beasts, an image largely imposed on them by the...

Study of 'spatial synchrony' using long-term data exposes ecological trends and could boost conservation, farming
Populations of animals and plants separated by even thousands of miles can rise and fall together...

Tick researchers identify new strain of Rickettsia bacteria that causes spotted fever infections in humans
In a residential backyard in Maine, Project ITCH researchers from the University of Massachusetts Amherst stumbled...

Wild bonobos study reveals that females team up to maintain power in their societies
Biologically speaking, female and male bonobos have a weird relationship. First, there's the sex. It's the...

Climate change is now the leading threat to imperiled species, new study finds
Authors of an article in BioScience reveal that climate change has become the most pervasive threat...

Global estimate finds mangrove forests nurture vast populations of commercially important marine species
An international team of researchers with a variety of backgrounds has worked together to calculate a...
Paying fishers to release endangered catches could aid conservation
A new study from the University of Oxford has revealed that an incentive program increased live...
Global map reveals seagrass meadows under threat—even inside protected areas
A new global analysis finds that many of the world's most threatened seagrass meadows lie within...
Yeast DNA reveals ties to human migration and the last ice age
Yeast is already a familiar ingredient to bakers and winemakers, but new research from the University...
What rattlesnake venom can teach us about evolution
Researchers at the University of South Florida are uncovering new clues about how animals evolve by...
Big brains and big ranges might not save birds from climate change
Biologists have long debated why some plants and animals can adjust to a wide range of...
Fishing bans can help kelp forests withstand marine heat waves
Marine heat waves that seemed extreme just a decade ago will become commonplace by the end...
Oil cleanup agents do not impede natural biodegradation, research reveals
Using spill-treating agents to clean up oil spills does not significantly hinder naturally occurring oil biodegradation,...
Insects are disappearing due to agriculture—and many other drivers, research reveals
Insects are disappearing at an alarming rate worldwide, but why? Agricultural intensification tops the list of...

Non-native trees gain ground in eastern US, reducing native species diversity
In the largest study of its kind, researchers at the Florida Museum of Natural History have...
Discovering 'pirate parasitism': Wasps can successfully exploit unsuitable hosts with help from another species
Parasitoid wasps sometimes lay eggs in unsuitable host insects, a behavior that has traditionally been considered...
Curious isolation: New butterfly species discovered
In the heart of Canada's Rocky Mountains, an unassuming yet remarkable butterfly has been quietly flying...
Simulations predict how pesticides may affect honeybee colonies
Honeybees are essential pollinators for agriculture and natural ecosystems. Stressors like climate change, habitat loss and...
A new record for California's highest-elevation tree: Jeffrey pine found in High Sierra
UC Davis Professor Hugh Safford was hiking for pleasure in California's High Sierra when he stumbled...
Personality test for bees: Research reveals differences in honey bee defense behavior within same colony
Researchers from the Cluster of Excellence Collective Behavior at the University of Konstanz have discovered that...
Gorillas in Congo's Nouabalé-Ndoki National Park scratch the ground for truffles, not for insects as long assumed
A recently published paper reveals that soil scratching by gorillas in Congo's Nouabalé-Ndoki National Park is...
Team captures first confirmed footage of a baby colossal squid
An international team of scientists and crew on board Schmidt Ocean Institute's research vessel Falkor (too)...
Woodrats' immunity to snake venom changes with the weather, researchers discover
The power of a rattlesnake's venom to incapacitate its prey may depend on more than just...

New pollen-replacing food for honey bees brings hope for survival
Scientists have unveiled a new food source designed to sustain honey bee colonies indefinitely without natural...

Foraging on the wing: How can ecologically similar birds live together?
A spat between birds at a backyard birdfeeder highlights the sometimes fierce competition for resources that...
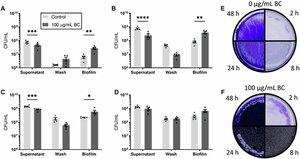
Bumble bee decline tied to air pollution's disruption of gut microbiome
A study of bumble bees has uncovered a potential reason for the insects' decline. By studying...
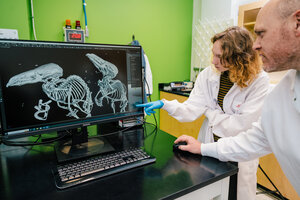
Shrews shrink in winter to conserve energy, study finds
Newly published research from UNC Greensboro biology professor Dr. Bryan McLean and colleagues shows that the...
To avoid parasites, some fruit flies sacrifice sleep
If you think doomscrolling leads to sleepless nights, imagine waking up in bed with a blood-sucking...